Energy Saving Mechanisms For Mac
Lenges through the introduction of novel mechanisms for adaptive. Energy efficient MAC protocols, EM-MAC uses no control channel and enables a node to. Aug 1, 2018 - To avoid wasting the limited energy, various energy saving mechanisms are proposed for MAC protocols. These mechanisms have a common. “Saving energy will always require a dual effort from students as well as teachers,” TeachThought stated. “By teaching students of energy saving through the tips mentioned above, you’ll be able to reduce energy consumption of your institute and your students will be able to reduce their energy bills.”.
Abstract Most multiple access collision avoidance-based (MAC) protocols for WLAN systems have been using fixed transmission power and have not considered energy-saving techniques targeted on channel estimation models. In order to prolong battery life and to improve the overall throughput performance of such systems, a novel PHY-MAC cross-layer energy-saving mechanism based on a distributed queuing MAC protocol and fuzzy logic theory is introduced for WLAN systems. Computer simulations have been performed and values for the throughput maximum performance and energy consumption have been obtained as a function of different scenario parameters. These values show that the throughput outperforms the one obtained with the IEEE 802.11 standard while reducing the energy consumption.Peer ReviewedPostprint (published version.

Energy Saving Mechanisms For Mac Pro
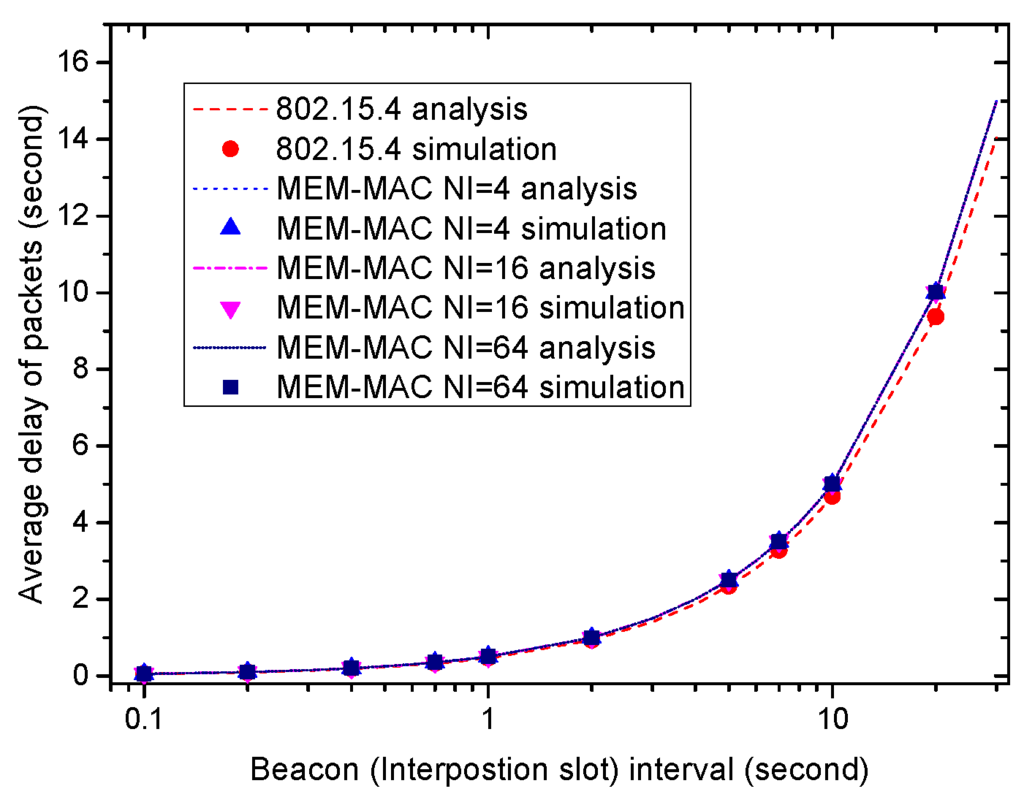
1, 2, 3 and 2 1Department of Mobile Communications Engineering, Changshin University, 262 Paryong-ro, Masanhoiwon-gu, Changwon-si, Gyeongsangnam-do 630-764, Republic of Korea 2Department of Computer Engineering, Kyung Hee University, 1732 Deogyeong-daero, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do 446-701, Republic of Korea 3The Aerospace Strategy & Technology Institute, Yonsei University, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-749, Republic of Korea Received 27 November 2014; Accepted 29 January 2015 Academic Editor: Sanghyuk Lee. Abstract This paper presents a novel and sustainable medium access control (MAC) scheme for wireless sensor network (WSN) systems that process high-dimensional aggregated data.
Based on a preamble signal and buffer threshold analysis, it maximizes the energy efficiency of the wireless sensor devices which have limited energy resources. The proposed group management MAC (GM-MAC) approach not only sets the buffer threshold value of a sensor device to be reciprocal to the preamble signal but also sets a transmittable group value to each sensor device by using the preamble signal of the sink node.
Energy Saving Mechanisms For Machines
The primary difference between the previous and the proposed approach is that existing state-of-the-art schemes use duty cycle and sleep mode to save energy consumption of individual sensor devices, whereas the proposed scheme employs the group management MAC scheme for sensor devices to maximize the overall energy efficiency of the whole WSN systems by minimizing the energy consumption of sensor devices located near the sink node. Performance evaluations show that the proposed scheme outperforms the previous schemes in terms of active time of sensor devices, transmission delay, control overhead, and energy consumption. Therefore, the proposed scheme is suitable for sensor devices in a variety of wireless sensor networking environments with high-dimensional data aggregate.